The Ultimate Guide to Laminated Plywood: Benefits, Uses, and FAQs.
Laminated plywood is a versatile and durable material that has become a staple in construction, furniture making, and interior design. Its unique composition and layered structure make it an excellent choice for a wide range of applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about laminated plywood, including its benefits, uses, types, and frequently asked questions.
What is Laminated Plywood?
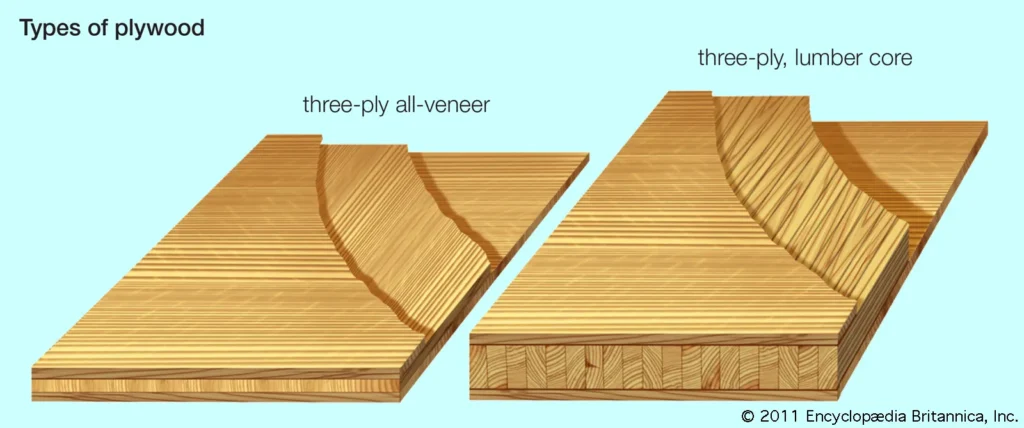
Laminated plywood is a type of engineered wood that consists of multiple layers of wood veneers bonded together with adhesive. The outer layers are typically covered with a decorative laminate, which enhances the material’s appearance and provides additional protection against wear and tear.
Composition of Laminated Plywood
- Core Layers: The core of laminated plywood is made up of several layers of wood veneers. These layers are arranged in a cross-grain pattern, which adds strength and stability to the material.
- Adhesive: High-quality adhesive is used to bond the layers together. This adhesive is typically waterproof, making laminated plywood resistant to moisture and humidity.
- Laminate Surface: The outer surface is covered with a decorative laminate, which can be customized to mimic the appearance of various materials, such as wood, stone, or metal.
Benefits of Laminated Plywood
Laminated plywood offers numerous advantages, making it a preferred choice for various applications. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Durability
Laminated plywood is known for its exceptional durability. The cross-grain construction and high-quality adhesive make it resistant to warping, cracking, and splitting. This makes it an ideal material for both indoor and outdoor use.
2. Moisture Resistance
The waterproof adhesive used in laminated plywood makes it highly resistant to moisture and humidity. This property is particularly beneficial for applications in kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor furniture.
3. Aesthetic Appeal
The decorative laminate surface can be customized to match any design aesthetic. Whether you prefer the look of natural wood, stone, or metal, laminated plywood can be tailored to meet your design needs.
4. Cost-Effective
Compared to solid wood, laminated plywood is more affordable while still offering similar aesthetic and functional benefits. This makes it a cost-effective option for large-scale projects.
5. Ease of Maintenance
Laminated plywood is easy to clean and maintain. The laminate surface is resistant to stains, scratches, and fading, ensuring that it retains its appearance over time.

Types of Laminated Plywood
There are several types of laminated plywood available, each suited for specific applications. Here are some of the most common types:
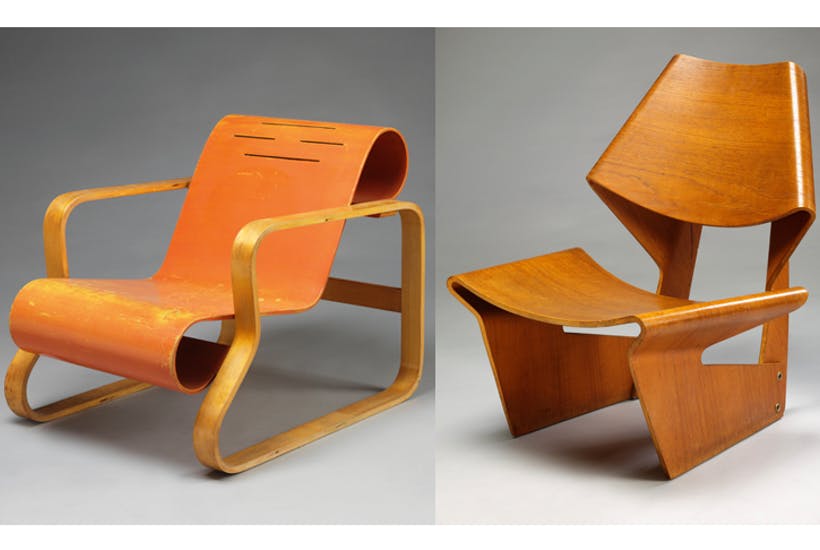
1. Decorative Laminated Plywood
This type of laminated plywood is primarily used for aesthetic purposes. It features a decorative laminate surface that can mimic the appearance of various materials, such as wood, stone, or metal. It is commonly used in furniture, cabinetry, and interior design.
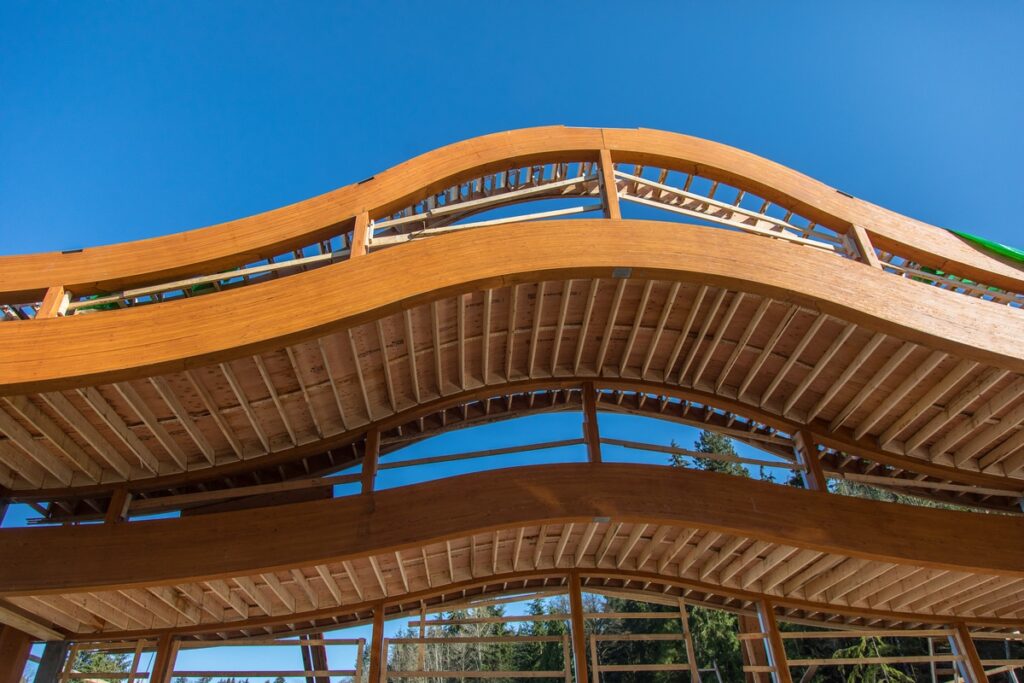
2. Structural Laminated Plywood
Structural laminated plywood is designed for load-bearing applications. It is used in construction for beams, columns, and other structural elements. This type of plywood is engineered to provide maximum strength and stability.
3. Marine Laminated Plywood
Marine laminated plywood is specifically designed for use in marine environments. It is made with waterproof adhesive and is resistant to rot, making it ideal for boat building, docks, and other water-related applications.
4. Fire-Retardant Laminated Plywood
Fire-retardant laminated plywood is treated with chemicals that make it resistant to fire. It is commonly used in commercial buildings, schools, and hospitals where fire safety is a priority.

Applications of Laminated Plywood
Laminated plywood is a versatile material that can be used in a wide range of applications. Here are some of the most common uses:
1. Furniture Making
Laminated plywood is widely used in the manufacture of furniture, including tables, chairs, cabinets, and shelves. Its durability and aesthetic appeal make it a popular choice for both residential and commercial furniture.
2. Interior Design
In interior design, laminated plywood is used for wall paneling, flooring, and ceiling applications. Its customizable surface allows designers to create unique and visually appealing spaces.
3. Construction
Laminated plywood is used in construction for structural elements such as beams, columns, and roofing. Its strength and stability make it an ideal material for load-bearing applications.
4. Cabinetry
Laminated plywood is commonly used in the manufacture of kitchen and bathroom cabinets. Its moisture resistance and durability make it well-suited for these environments.
5. Marine Applications
Marine laminated plywood is used in boat building, docks, and other marine structures. Its resistance to water and rot makes it an ideal material for these applications.

How to Choose the Right Laminated Plywood
Choosing the right laminated plywood for your project is crucial to ensure the best results. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Application
Consider the specific application for which you need laminated plywood. For example, if you are building furniture, decorative laminated plywood may be the best choice. For structural applications, opt for structural laminated plywood.
2. Grade
Laminated plywood is available in different grades, which indicate the quality of the material. Higher-grade plywood is more expensive but offers better durability and appearance.
3. Thickness
The thickness of laminated plywood can vary depending on the application. Thicker plywood is more durable and suitable for load-bearing applications, while thinner plywood is ideal for decorative purposes.
4. Laminate Type
Consider the type of laminate surface you need. Some laminates are more resistant to scratches and stains, while others offer a more realistic appearance of natural materials.
5. Budget
Laminated plywood is available at various price points. Determine your budget and choose a product that offers the best balance of quality and cost.
Maintenance and Care of Laminated Plywood
Proper maintenance and care can extend the lifespan of laminated plywood and keep it looking its best. Here are some tips:
1. Cleaning
Regularly clean the surface of laminated plywood with a soft cloth and mild detergent. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or scrubbers, as they can damage the laminate surface.
2. Avoid Excessive Moisture
While laminated plywood is moisture-resistant, prolonged exposure to water can cause damage. Wipe up spills immediately and avoid using laminated plywood in areas with constant water exposure.
3. Protect from Scratches
Use felt pads or coasters under heavy objects to prevent scratches on the laminate surface. Avoid dragging sharp or heavy objects across the surface.
4. Regular Inspection
Periodically inspect laminated plywood for signs of wear or damage. Address any issues promptly to prevent further deterioration.

Environmental Impact of Laminated Plywood
Laminated plywood is considered an environmentally friendly material due to its sustainable production process. Here are some reasons why:
1. Sustainable Sourcing
The wood veneers used in laminated plywood are typically sourced from sustainably managed forests. This ensures that the production of laminated plywood does not contribute to deforestation.
2. Recyclable
Laminated plywood can be recycled at the end of its lifespan. The wood veneers can be repurposed, and the laminate surface can be removed and recycled separately.
3. Low VOC Emissions
The adhesives used in laminated plywood are low in volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it a safer choice for indoor air quality.
4. Energy-Efficient Production
The production process of laminated plywood is energy-efficient, with minimal waste generated. This reduces the overall environmental impact of the material.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between laminated plywood and regular plywood?
Laminated plywood has a decorative laminate surface that enhances its appearance and provides additional protection. Regular plywood does not have this laminate layer and is typically used for structural applications.
2. Can laminated plywood be used outdoors?
Yes, laminated plywood can be used outdoors, especially if it is marine-grade. However, it is important to ensure that the edges are properly sealed to prevent moisture penetration.
3. Is laminated plywood waterproof?
Laminated plywood is moisture-resistant but not entirely waterproof. Marine-grade laminated plywood is more resistant to water and is suitable for marine applications.
4. How do I clean laminated plywood?
Clean laminated plywood with a soft cloth and mild detergent. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or scrubbers, as they can damage the laminate surface.
5. Can laminated plywood be painted?
Yes, laminated plywood can be painted, but it is important to sand the surface lightly and use a primer designed for laminate surfaces to ensure proper adhesion.
6. What is the lifespan of laminated plywood?
The lifespan of laminated plywood depends on the quality of the material and the conditions in which it is used. With proper care and maintenance, laminated plywood can last for many years.
7. Is laminated plywood eco-friendly?
Yes, laminated plywood is considered eco-friendly due to its sustainable sourcing, recyclability, and low VOC emissions.
8. Can laminated plywood be used for flooring?
Yes, laminated plywood can be used for flooring, especially in areas with low to moderate foot traffic. It is important to choose a high-grade plywood with a durable laminate surface.
9. What are the disadvantages of laminated plywood?
Some disadvantages of laminated plywood include its susceptibility to edge chipping, limited repairability, and the potential for delamination if not properly maintained.
10. How do I choose the right thickness of laminated plywood?
The thickness of laminated plywood depends on the application. For structural applications, thicker plywood is recommended, while thinner plywood is suitable for decorative purposes.
Conclusion
Laminated plywood is a versatile, durable, and cost-effective material that offers numerous benefits for a wide range of applications. Whether you are building furniture, designing interiors, or working on a construction project, laminated plywood is an excellent choice. By understanding its properties, types, and maintenance requirements, you can make the most of this remarkable material.
By following this comprehensive guide, you now have a thorough understanding of laminated plywood, its benefits, uses, and how to choose the right type for your needs. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional builder, laminated plywood is a material that can help you achieve your project goals with ease and efficiency.